TMJ-Related Tinnitus Treatment Clinic
TMJ therapy can often help reduce or even eliminate tinnitus, especially when the tinnitus is directly linked to temporomandibular joint dysfunction. Treatment for TMJ-related tinnitus typically focuses on alleviating the underlying joint issues, which can significantly decrease the pressure and tension affecting the ear. For more information, please contact us today or book an appointment online now! We have convenient locations in Peoria/Dunlap IL, Bloomington IL, Wausau WI, and El Paso TX.


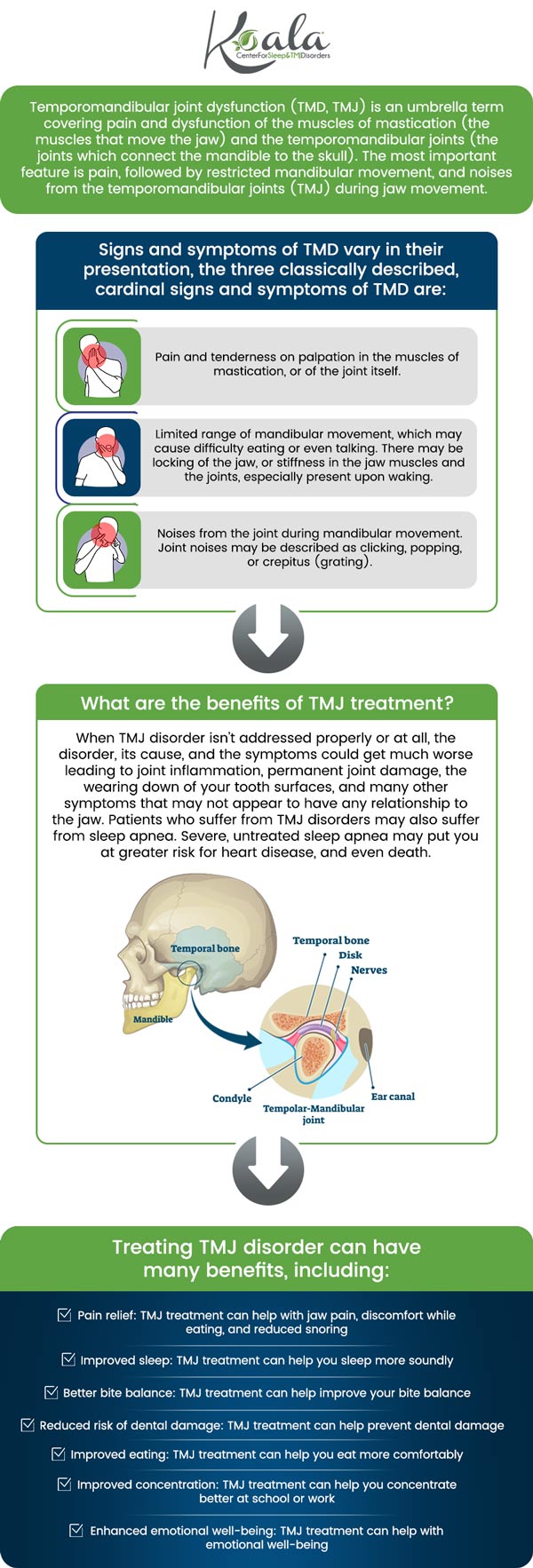
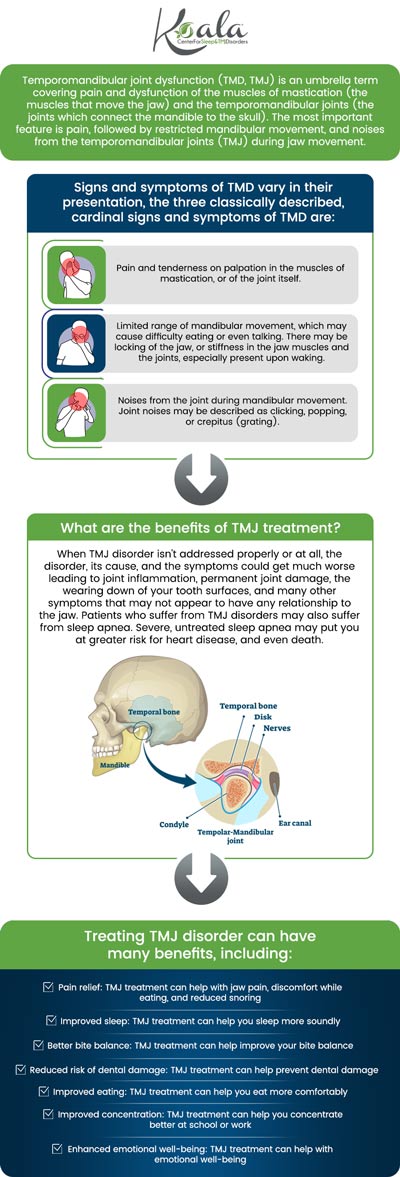
Table of Contents:
How does TMJ lead to ringing in the ears?
How is TMJ-related ringing in the ears diagnosed?
Can TMJ therapy help reduce or eliminate tinnitus?
Is TMJ-related tinnitus more common in certain age groups?
TMJ disorders can lead to ringing in the ears owing to the close proximity between the temporomandibular joint and the ear. When an individual experiences dysfunction or misalignment in the TMJ, it can create pressure on the structures surrounding the ear, including the nerves and muscles. This pressure can disrupt normal auditory processing, leading to the perception of ringing or buzzing sounds. Additionally, the muscles responsible for controlling jaw movement can become tense or inflamed, further contributing to tinnitus as the ear and jaw are closely connected through shared neural pathways. The exact mechanisms linking TMJ to tinnitus are complex, but it is widely recognized that inflammation, nerve irritation, and muscle tension caused by TMJ disorders can significantly influence the ear. TMJ-related tinnitus often occurs alongside other symptoms such as jaw pain, headaches, and ear discomfort. Addressing the underlying TMJ issue through therapy and other interventions can help alleviate the pressure on the ear structures and reduce the occurrence of tinnitus.
Diagnosing TMJ-related tinnitus typically begins with a comprehensive evaluation by an expert in TMJ disorders. The process includes a thorough medical history, an examination of the jaw and bite alignment, and an assessment of the patient’s symptoms, including any noises in the ears. Imaging studies may be used to evaluate the temporomandibular joint’s structure and detect any signs of dysfunction or inflammation. Sometimes, the evaluation involves specific jaw movement tests to assess how TMJ activity may be affecting the ears. In some cases, patients are referred to audiologists to rule out other potential causes of tinnitus, such as hearing loss or neurological issues. Once TMJ is identified as the likely source of tinnitus, the specialist will develop a tailored treatment plan to address both the joint dysfunction and the auditory symptoms. A proper diagnosis is critical for effective treatment since TMJ-related tinnitus can mimic other ear-related conditions, making early detection essential for relief.
TMJ therapy can often help reduce or even eliminate tinnitus, especially when the tinnitus is directly linked to temporomandibular joint dysfunction. Treatment for TMJ-related tinnitus typically focuses on alleviating the underlying joint issues, which can significantly decrease the pressure and tension affecting the ear. Common therapeutic approaches include the use of custom dental appliances like splints or mouthguards that help align the jaw and reduce strain on the TMJ. Physical therapy exercises targeting the muscles surrounding the jaw and neck can also be highly effective in relieving tension. The goal of TMJ therapy is to address the root cause of the joint dysfunction, and as the jaw’s function improves, many patients experience a noticeable decrease in tinnitus. While not every case of TMJ-related tinnitus can be fully resolved, appropriate therapy can often provide significant relief and improve overall quality of life.
TMJ-related tinnitus can affect individuals across various age groups, but it may be more prevalent in certain populations due to lifestyle factors and age-related changes in joint health. Younger adults who experience high levels of stress, poor posture, or habits like teeth grinding may be more prone to developing TMJ disorders, which in turn can lead to tinnitus. Additionally, individuals in middle age who experience wear and tear on their joints or have experienced trauma to the jaw are also at risk of developing TMJ-related tinnitus. Age-related factors, such as arthritis, can contribute to TMJ dysfunction in older adults, leading to an increased incidence of tinnitus in this group. However, TMJ-related tinnitus is not confined to one particular age group. It can be triggered by stress, trauma, or chronic jaw misalignment at any stage of life. Recognizing these risk factors and seeking early intervention can help reduce the impact of TMJ disorders on ear health across all age groups.

Additional Services You May Need
▸ KoalaKIDZzz®
▸ Sleep Apnea
▸ Snoring
▸ TMJ Disorder
▸ Fatigue
▸ Sleep Disorders
▸ Weight Loss
▸ CPAP Alternative
▸ Oral Appliances